Understanding STVZO Bike Light Pattern and Optical Design
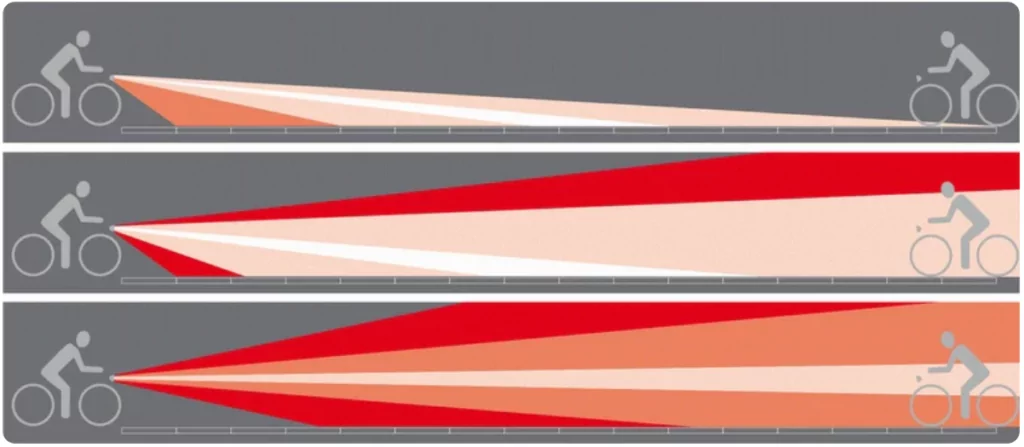
STVZO (Straßenverkehrs-Zulassungs-Ordnung) is one of the most critical standards in the realm of bicycle lighting, ensuring compliance with legal requirements while enhancing the safety and convenience of cyclists. Adhering to these stringent standards is essential for providing effective illumination and meeting the necessary regulations for bike lights. Designing an STVZO-compliant light involves a deep understanding […]
How does a light pipe overmold work?
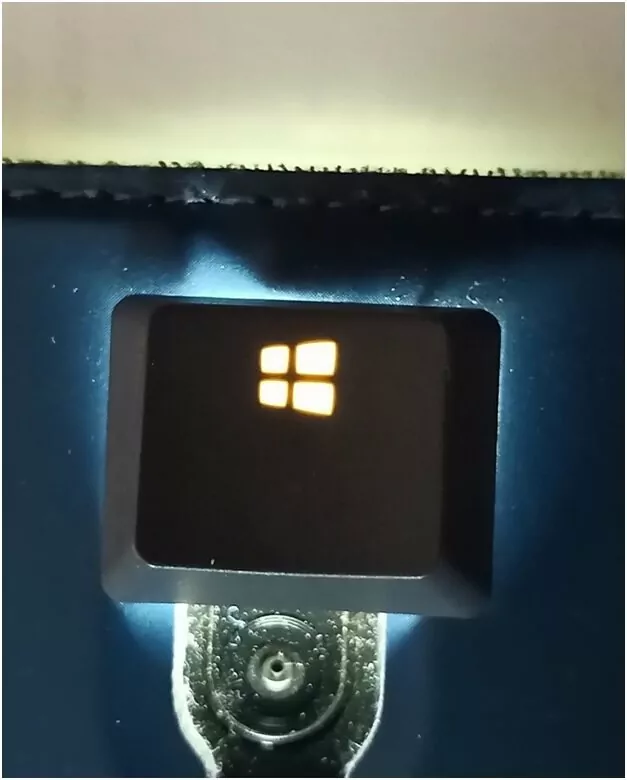

One common production method for light pipes is the overmold . This method uses an inexpensive light diffused plastic overmolded with a black case to generate a light-pipe. The “Win” keyboard key is one good example. “Win” key appearance to the observer. The black key body has a hole; during manufacturing, this hole is filled […]
Optimized Solutions for Underwater Optics Design

Underwater optics play a crucial role in the design of underwater camera lenses, where a large number of variables come into play. As with every optical system design, the selection of cameras, lenses, housings, and operational parameters greatly influences the performance of the complete system. Determining the correct combination of components is what experienced optical […]
Variable spot size + color mixing optical system
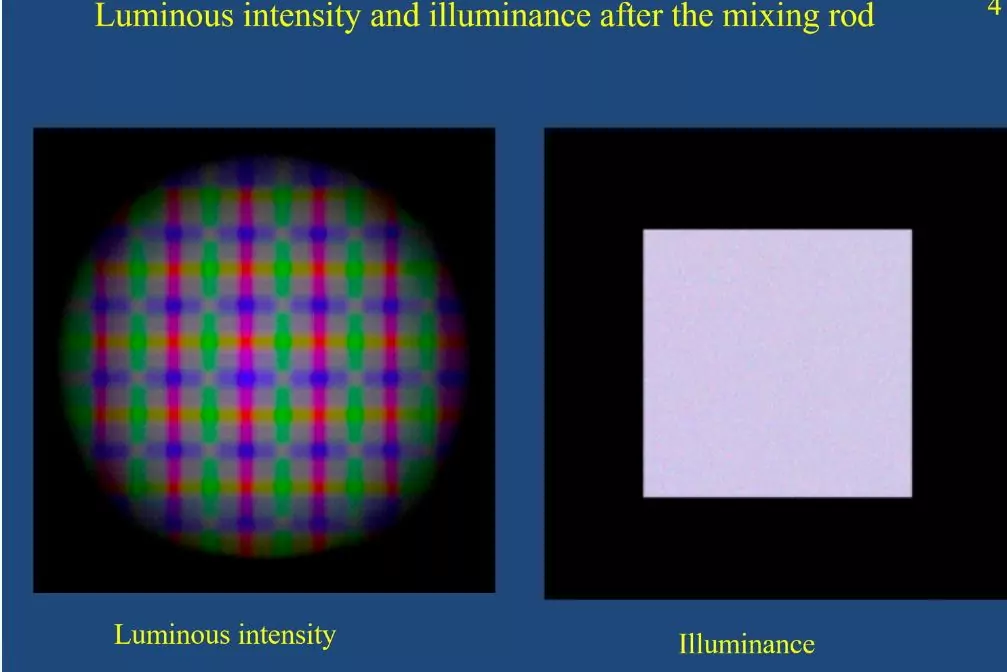

In applications like concert show lighting, architectural lighting, and cinema projection, achieving good color mixing and variable spot size is essential. The optics design in front of a RGBW LED source must include optimization for color uniformity as well as beam shape. A common solution is to place diffuse materials in the optical path. This […]
Conoscopic Lens Design
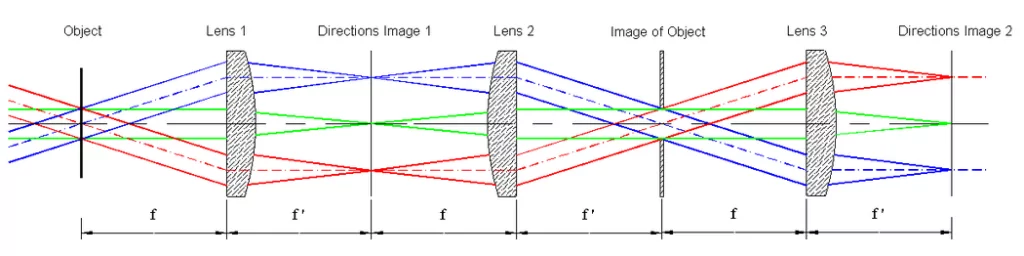
A conoscopic lens is an instrument that can be used to measure the angular distribution of a light source. Its use is quite different from a lens, as in photography. An image created by a conoscopic lens resembles that of a fisheye lens. That is a highly distorted image. Conoscopic lenses are used to evaluate […]
Non-sequential ray tracing
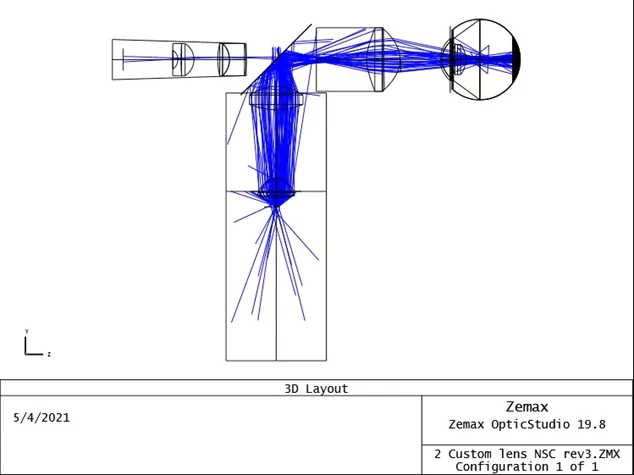
When doing optical simulations using a program like ZEMAX, we can choose to do our simulations using two modes: sequential and non-sequential optics. Sequential optics, as the name indicates, follows the optical path of light as it goes from one surface to the next. For example in Cooke Triplet shown in Figure 1, light travels […]